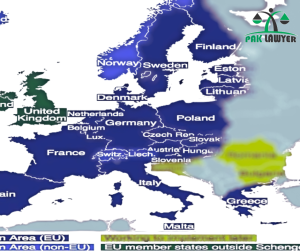
Introduction:
A Schengen Visa opens the door to exploring the vibrant cultures and picturesque landscapes of the Schengen Area. Comprising numerous European countries with eliminated internal border controls, this short-stay visa allows visitors to enjoy a 90-day stay within a 180-day period. As you embark on this exciting journey, it’s crucial to be well-prepared with the necessary documents. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key requirements for a Schengen Visa application.
Schengen Visa Requirements:
1. Fully Completed Application Form:
Begin your journey by filling out the Schengen Visa application form. Ensure all sections are completed accurately and sign the form before submission.
2. Passport and Photographs:
Submit a valid passport with more than three months’ validity, and make sure it has at least two blank pages for visa affixing. Include two recent passport-sized photographs meeting Schengen visa specifications.
3. Itinerary and Accommodation:
Provide a detailed itinerary of your trip, including round-trip reservations or flight details. For accommodation, a confirmed hotel reservation is required. If staying with relatives or friends, proof of accommodation and their details may be requested.
4. Visa Application Fee:
Include proof of payment for the Schengen Visa application fee, which is €80 for adults and €40 for children aged 6 to 12.
5. Travel and Medical Insurance:
Demonstrate proof of travel and medical insurance with coverage of up to €30,000 for potential medical expenses during your stay.
6. Financial Means:
Show evidence of financial means through a bank account statement (no older than three months) indicating sufficient funds to cover your stay. If sponsored, include a sponsorship letter and the sponsor’s recent bank statement.
Additional Requirements:
1. Proof of Employment:
If employed, provide a letter from your company stating your monthly wages, job continuity after leave, and the duration of your vacation.
2. No Objection Letter:
Include a no objection letter if required by the authorities.
3. Student Status:
For students, submit a letter from your school/college/university confirming your attendance.
Special Cases:
1. Visiting Family or Friends:
Include an invitation letter from your host, along with proof of your relationship and details of your stay.
2. Business Travel:
If traveling for business, present a letter from your employer outlining the purpose of your visit. Invitations from a Schengen-based company should include the event details.
3. Studying in Europe:
Provide an acceptance letter from the institution you plan to attend, specifying details of your stay.
4. Event Attendance:
For event participation, submit an invitation letter, event details, and proof of the necessity of your presence.
5. Retirement:
If retired, present six months of pension statements as proof of financial capability.
Minors’ Visa Requirements:
For minors, additional documents include the child’s birth certificate, signed applications from both parents, family court orders (if applicable), certified copies of parents’ passports, and a notarized letter of parental authorization if the child is traveling alone.
Conclusion:
Understanding the specific requirements for your Schengen Visa application is crucial for a smooth and successful process. Ensure that you have all necessary documents in order to embark on your European adventure with confidence.
For more information, please, Ask your question here.
Key Responsibilities of an FDA Lawyer.
Understanding Complex Regulations:
FDA regulations are intricate and subject to frequent changes. An experienced lawyer possesses the knowledge to interpret and apply these regulations effectively.
Navigating Approval Processes:
From 510(k) submissions to Pre-market Approval (PMA) applications, an FDA lawyer guides manufacturers through the approval processes, ensuring compliance at every step.
Ensuring Compliance with Quality Systems
Quality is non-negotiable in the medical device industry. An FDA lawyer aids in developing and maintaining robust quality systems to meet regulatory standards.
Expertise in Classification and Labeling
Importance of Correct Device Classification
Correctly classifying a medical device is fundamental. An experienced lawyer ensures accurate classification, avoiding pitfalls and delays in the approval process.
Role in Accurate Product Labeling
Clear and precise labeling is crucial for communicating device specifications and safety information. An FDA lawyer assists in crafting compliant and effective product labels.
Navigating the Pre-market Approval (PMA) Process
Overview of PMA Requirements:
The PMA process is rigorous, requiring comprehensive data and analysis. A seasoned FDA lawyer provides insights into fulfilling PMA requirements efficiently.
Strategies to Expedite the Approval Process
Time is often of the essence in the medical device industry. Legal strategies to expedite the PMA process without compromising quality are a key focus.
Ensuring Post-market Compliance
Monitoring and Reporting Adverse Events
Post-market surveillance is critical. An FDA lawyer aids in establishing robust systems for monitoring and reporting adverse events promptly.
Handling Recalls and Corrective Actions
In the unfortunate event of a product recall, legal expertise becomes paramount. An experienced lawyer navigates the recall process and mitigates legal risks.
Risk Management Strategies
Assessing and Mitigating Potential Risks
Identifying and mitigating risks early in the development process is essential. An FDA lawyer collaborates with manufacturers to implement effective risk management strategies.
Developing Comprehensive Risk Management Plans
Creating comprehensive risk management plans not only ensures compliance but also enhances the safety and reliability of medical devices.
International Regulatory Affairs
Managing Global Regulatory Requirements
For manufacturers operating globally, an FDA lawyer aids in harmonizing regulatory efforts, ensuring compliance with diverse international standards.
Harmonizing Compliance Efforts Across Regions
Navigating different regulatory landscapes can be challenging. Legal support ensures a cohesive and compliant approach across various regions.
Legal Support During FDA Inspections
Preparing for FDA Inspections
Anticipating and preparing for FDA inspections is vital. An experienced FDA lawyer guides manufacturers in preparing thorough documentation and responses.
Addressing Findings and Potential Violations
In the aftermath of an inspection, legal representation becomes crucial in addressing findings and potential violations.
Addressing Enforcement Actions
Responding to Warning Letters and FDA Notices
Receiving a warning letter or notice from the FDA can be daunting. Legal expertise is essential to craft effective responses and corrective action plans.
Legal Representation in Disputes and Litigation
In the unfortunate event of disputes or litigation, an experienced FDA lawyer provides strong legal representation, safeguarding the interests of the manufacturer.
Cost-Effective Regulatory Solutions
Balancing Legal Support with Budget Considerations
Effective regulatory compliance doesn’t have to break the bank. An experienced FDA lawyer helps manufacturers balance legal support with budget constraints.
Choosing Cost-Effective Regulatory Strategies
Strategic planning and legal guidance result in cost-effective regulatory solutions without compromising on quality or compliance.
Recent Changes in FDA Regulations
Highlighting Recent Updates in Medical Device Regulations
The regulatory landscape is dynamic, with frequent updates. Staying informed about recent changes is essential for manufacturers and their legal teams.
Implications for Manufacturers and Legal Strategies
Understanding the implications of regulatory changes is key. An FDA lawyer adapts legal strategies to align with the evolving regulatory environment.
Collaboration with Other Industry Experts
Importance of Working with Regulatory Consultants and Specialists
In addition to legal expertise, collaboration with regulatory consultants and specialists enhances the overall regulatory strategy.
Building a Comprehensive Regulatory Team
A well-rounded regulatory team, including legal and industry experts, strengthens a manufacturer’s ability to navigate complex regulatory challenges.
Case Studies: Successful FDA Approvals
Showcasing Real-World Examples of Successful Regulatory Strategies
Examining case studies provides valuable insights into successful FDA approvals, shedding light on effective strategies employed by manufacturers and their legal teams.
Learning from Challenges and Triumphs
Analyzing challenges and triumphs in FDA approvals helps manufacturers proactively address potential obstacles in their regulatory journey.
Tips for Choosing an Experienced FDA Lawyer
Qualities to Look for in Legal Expertise
Choosing the right FDA lawyer is critical. Look for qualities such as experience, industry knowledge, and a successful track record in medical device regulations.
Considerations for a Successful Attorney-Client Relationship
A successful attorney-client relationship is built on communication, trust, and a shared commitment to achieving regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
In the complex landscape of FDA regulations for medical devices, an experienced FDA lawyer is an indispensable partner for manufacturers. Their expertise not only ensures compliance but also facilitates a smoother regulatory journey, allowing manufacturers to focus on innovation and patient safety.
FAQs
-
Why is an experienced FDA lawyer crucial for medical device manufacturers?
-
An experienced FDA lawyer navigates complex regulations, ensuring compliance and timely approvals.
-
-
What role does an FDA lawyer play in post-market compliance?
-
An FDA lawyer assists in monitoring adverse events, handling recalls, and maintaining post-market compliance.
-
-
How can manufacturers benefit from recent changes in FDA regulations?
-
Staying informed about recent changes helps manufacturers adapt their strategies and stay ahead in compliance.
-
-
What are the key considerations when choosing an FDA lawyer?
-
Look for experience, industry knowledge, and a successful track record in medical device regulations.
-
-
How does legal support during FDA inspections benefit manufacturers?
-
Legal support helps manufacturers prepare for inspections and address findings effectively.
-
Halala Marriage in Pakistan
Introduction:
Nikah Halala, also known as intervening marriage, is a controversial practice in Islamic law, raising ethical and legal questions. This article delves into the concept of Halala, examining its definition, the Quranic perspective, Sunnah teachings, and the viewpoints of different Islamic jurists. Additionally, it explores the legal status of Halala marriages under the Muslim Family Laws Ordinance, 1961, and references significant judgments from the Federal Shariat Court.
Understanding Nikah Halala:
Nikah Halala is a process wherein a divorced wife, after the pronouncement of the third irrevocable divorce, becomes lawful to her former husband. The husband cannot remarry her directly; instead, the wife must enter into an intervening marriage with another man. This intervening marriage concludes either through consummation and subsequent divorce or the death of the second husband. After observing the required waiting period (Iddah), the divorced couple can reunite.
Quranic Perspective and Sunnah Teachings:
The Quran explicitly addresses Nikah Halala in Surah Al-Baqarah (2:230), stating that if a man divorces his wife for the third time, she is not lawful to him until she marries another husband. However, it is crucial that this marriage be valid, and temporary marriages (mut’ah) or marriages solely for the purpose of making the woman permissible for her first husband (tahleel) are deemed haraam (forbidden).
Prophet Muhammad’s teachings, as recorded in saheeh ahaadeeth, further emphasize the prohibition of Nikah Halala, referring to those involved as accursed.
Jurisprudential Viewpoints:
1. Hanafi Jurists: While considering Nikah Halala valid, Hanafi jurists label it as abominable and improper (makruh). However, there is dissent within this school of thought, with some scholars asserting its invalidity. Notably, Imam Abu Yousef holds the view that Nikah Halala is invalid.
2. Shafi’i Jurists: Shafi’i jurists argue that the validity of Nikah Halala depends on whether the marriage contract includes a condition for subsequent divorce. Agreements made before or after the marriage contract, without such a condition, are considered valid.
3. Maliki and Hanbali Jurists: Both Maliki and Hanbali jurists deem Nikah Halala, intended to facilitate re-marriage between a divorced couple, as invalid. They emphasize the disobedience to God’s laws and the ineffectiveness of using an intermediary for this purpose.
Legal Status under Muslim Family Laws Ordinance, 1961:
Section 7(6) of the Muslim Family Laws Ordinance, 1961, explicitly allows a wife, whose marriage has been terminated by talaq under this section, to re-marry the same husband without an intervening marriage unless the termination has occurred for the third time.
Notable Judgments:
1. Federal Shariat Court Judgment (2014 PLD 43 FEDERAL-SHARIAT-COURT):
This landmark judgment held that “Khula” and “Mubarat” operate as a single, irrevocable divorce. Both spouses can contract a fresh marriage with mutual consent, without the need for an intermediary marriage.
2. Federal Shariat Court Judgment (1994 PCRLJ 1856 FEDERAL-SHARIAT-COURT):
This case highlighted the legal consequences of living together after non-withdrawal of divorce. While cohabitation without remarriage amounted to Zina, the court reduced the sentences considering the accused’s lack of awareness.
Conclusion:
Nikah Halala remains a subject of debate within Islamic jurisprudence, with varying viewpoints on its validity and ethical considerations. Understanding its legal and Sharia status involves an intricate analysis of Quranic verses, Sunnah teachings, and interpretations by different juristic schools. The Muslim Family Laws Ordinance, 1961, provides clarity on the permissibility of re-marrying the same husband without an intervening marriage in certain circumstances. Landmark legal judgments further contribute to shaping the discourse around Nikah Halala, highlighting the complexity of balancing religious principles with contemporary legal frameworks.
Divorce procedure in Pakistan
The divorce procedure in Pakistan for husbands is a comprehensive process involving several detailed steps:
1. Initiation of Divorce Deed: The husband initiates the divorce proceedings by formally executing a divorce deed on stamp paper valued at Rs.300. This crucial document serves as a legally binding pronouncement of divorce in written form, with the husband expressing his intent to divorce his wife. Collaboration with a qualified lawyer is often sought to ensure the legal validity and comprehensive preparation of this document.
2. Dispatching Documents to Wife: Upon completion of the divorce deed, the husband proceeds to dispatch the original document to his wife. Accompanying the divorce deed, a copy of the divorce notice addressed to the Concerned Union Council is included. This copy of notice serves the dual purpose of informing the wife about the imminent divorce and providing information regarding the initiation of divorce proceedings in relevant Union Council.
3. Notice to Arbitration Council: The husband is obligated to formally notify the relevant Union Council/Arbitration Council in writing of his pronouncement of divorce upon his wife. This written communication includes a notice accompanied by a copy of the divorce deed, the Nikah Nama (marriage certificate), and a copy of the husband’s ID card. The Union Council or Arbitration Council assumes a pivotal role in overseeing the divorce proceedings, ensuring that all legal requirements are met during the course of the divorce.
4. Issuance of Reconciliation Notices: Upon receiving the Notice, the Arbitration Council issues formal notices to both the husband and wife, summoning them to attend reconciliation proceedings. These notices indicate the date, time, and venue for the reconciliation sessions.
5. Participation in Reconciliation Proceedings: Both parties involved in the divorce are given the option to attend the reconciliation proceedings either in person or through appointed representatives, such as family members or legal representatives. The objective of these sessions is to explore the possibility of resolving marital issues and preventing the divorce.
6. 90-Days Waiting Period: If reconciliation efforts prove unsuccessful, the Arbitration Council is bound to issue a divorce certificate. However, before the issuance of the certificate, a mandatory waiting period of 90 days must transpire. This waiting period is calculated from the date of the initial notice sent to the concerned Chairman of the Arbitration Council.
7. Divorce Certificate Issuance: After the completion of the 90-day waiting period, and in the absence of successful reconciliation, the Arbitration Council formally issues the divorce certificate. This certificate serves as legal documentation of the dissolution of the marriage.
8. Incorporation of Divorce in Nadra: The divorce certificate is issued following approval from the NADRA database. Upon receiving authorization from the NADRA system, the Union Council promptly issues the certificate, finalizing the documentation of the divorce proceedings. This ensures that the certificate aligns with and is officially recognized by the authoritative NADRA database, providing an accurate record of the divorce. However, it is imperative for both parties involved in the divorce to individually update their CNIC (Computerized National Identity Card) record or FRC (Family Registration Certificate) record at a NADRA office. This update is facilitated by presenting the issued Divorce Certificate to the NADRA authorities. This ensures that the divorce information is accurately reflected in the official records maintained by NADRA for each party.
This detailed process ensures that divorce in Pakistan is conducted in a systematic and legally sound manner, with provisions for reconciliation efforts and a mandatory waiting period to allow for careful consideration before finalizing the divorce. The divorce process for husbands in Pakistan is entirely distinct from the divorce procedure for wives in the Family Court.
For additional information, please visit our YouTube Channel.
Ensuring Women’s Safety: Navigating Challenges in the Age of Online Taxis
Introduction
In recent years, the use of online taxi services such as Uber, Careem, Indrive, and others has witnessed a substantial surge in Pakistan. These services provide a convenient and seemingly safer alternative to traditional taxis, garnering trust from parents who opt for them to ensure the safety of their daughters studying in schools and universities. Working women, too, have embraced these platforms as a reliable means of transportation. However, amid the growing popularity of online taxis, there have been instances of uneducated drivers causing issues related to pick and drop, credit card usage, and sometimes even harassment.
Challenges Faced by Passengers:
While the majority of online taxi rides transpire smoothly, there have been reports of troubling incidents involving drivers. Situations can escalate when unscrupulous drivers harass passengers, particularly women, and demand exorbitant fares. In some cases, drivers have been reported to lock their cabs, restricting the movement of female passengers, thus jeopardizing their safety.
Legal Perspective:
Such actions not only violate ethical standards but are also illegal under the provisions of Section 509 of the Pakistan Penal Code. This section specifically deals with harassment, stating that if anyone harasses a woman through words, gestures, or actions, they can be sentenced to imprisonment and fined. It is essential for passengers, especially women, to be aware of their rights and the legal consequences these drivers may face.
Police Intervention and Women Safety Application:
To address these concerns promptly, passengers are strongly encouraged to contact the police immediately if faced with any harassment or unsafe situations. The police have introduced a dedicated Women Safety Application for quick assistance. This application allows women to alert law enforcement in emergencies, enhancing their overall safety and security during rides.
Safety Features of Cab Applications:
Cab applications themselves come equipped with safety features that passengers, especially women, should be familiar with. These features allow users to share their real-time location with trusted contacts and even record conversations, serving as valuable evidence in case of any untoward incidents. By actively utilizing these safety measures, passengers can contribute to creating a more secure environment when using online taxis.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, while online taxi services offer convenience and a sense of security, it is crucial to be aware of potential challenges and take proactive steps to address them. By understanding their legal rights, using available safety applications, and leveraging the features embedded in cab applications, passengers, particularly women, can contribute to their own safety.
This article aims to raise awareness about the importance of women’s safety in society, emphasizing that incidents of harassment should not hinder their progress and active participation in the prosperity of our country. Let us collectively work towards creating a safer and more inclusive environment for everyone.
For more information contact Pak-Lawyer Associates
Citizenship of Pakistan for Foreign Spouses: Navigating Legal Terrain
Introduction:
The issue of granting Pakistani citizenship to foreign spouses has become a focal point in legal discussions, marked by recent judgments that shed light on the complexities surrounding this matter. This article endeavors to provide a comprehensive legal exploration of the topic, analyzing recent cases, the broader legal framework, and the procedural aspects involved in acquiring citizenship for foreign spouses in Pakistan.
Legal Landscape:
1. Constitutional Provisions:
Pakistan’s Constitution, adopted in 1973, lays the foundation for citizenship laws. The principle of equality before the law, as enshrined in Article 25, serves as a cornerstone in evaluating the constitutionality of citizenship-related statutes. Recent judicial pronouncements have brought attention to the need for constitutional alignment with international norms.
2. Citizenship Act, 1951:
The Citizenship Act, 1951, governs the acquisition and loss of Pakistani citizenship. Section 10(2) of the Act has been a focal point of legal scrutiny. It delineates different criteria for male and female foreign spouses seeking Pakistani citizenship, leading to allegations of gender-based discrimination.
Recent Judicial Developments:
1. Mst. Rukhsana Bibi and others v. Government of Pakistan (2017):
The Lahore High Court’s judgment in this case addressed the discriminatory nature of Section 10(2) of the Citizenship Act. The court declared the provision as violative of Article 25 of the Constitution, emphasizing the right of foreign spouses to be treated equally regardless of gender. This landmark decision underscores the judiciary’s commitment to eradicating gender-based disparities in citizenship matters. (PLJ 2017 Lahore 14)
2. Suo Moto Case No. 1/K of 2006 (Gender Equality):
The Federal Shariat Court’s decision in this case challenged the discriminatory application of Section 10(2) of the Citizenship Act. The court emphasized the need for legislative amendments to ensure gender equality in the acquisition of Pakistani citizenship by foreign spouses. This precedent adds weight to the call for legal reforms. (PLD 2008 Federal Shariat Court 1)
3. I.A. Sharwani and others v. Government of Pakistan (1991):
This Supreme Court decision interpreted Article 25 of the Constitution, establishing the principles of equal protection of the law. It emphasized that persons similarly situated should be treated alike, laying the groundwork for future discussions on gender equality in citizenship matters.
(1991 SCMR 1041)
4. Secretary Economic Affairs Division, Islamabad v. Anwar-ul-Haq Ahmed and others (2013):
In this Supreme Court judgment, principles related to equal protection of the law were reinforced. The court emphasized that reasonable classification is permissible but must be founded on a reasonable basis, setting standards for evaluating the constitutionality of citizenship laws.
(2013 SCMR 1687)
Procedural Aspects:
1. Citizenship Application:
Foreign spouses seeking Pakistani citizenship typically initiate the process by submitting a formal application to the relevant authorities. The application may require details about the marriage, background information, and reasons for seeking citizenship.
2. Documentation:
Applicants are usually required to submit a set of documents, including marriage certificates, passports, proof of residence, and any other documents deemed necessary by the authorities. These documents help establish the legitimacy of the marital relationship and the eligibility for citizenship.
3. Application Review:
Upon submission, the authorities review the application and supporting documents. This involves verifying the authenticity of the information provided and ensuring that the applicant meets the criteria outlined in the relevant laws.
4. Fee Payment:
In some cases, applicants may be required to pay processing fees. The fee structure is determined by the relevant authorities and is subject to change. The payment is often a prerequisite for the application to be considered.
5. Oath of Allegiance:
If the application is approved, the foreign spouse may be required to take an oath of allegiance to Pakistan. This formalizes the commitment to abide by the laws and principles of the country.
6. Citizenship Ceremony:
Successful applicants may be invited to a citizenship ceremony, where they officially receive their Pakistani citizenship certificate. This ceremony may include the administration of the oath of allegiance in a formal setting.
Legal Implications:
1. Gender Equality:
Recent judgments, including those by the Lahore High Court and the Federal Shariat Court, highlight the imperative of ensuring gender equality in citizenship laws. The principles established in these cases have set a strong foundation for challenging discriminatory provisions.
2. International Commitments:
Pakistan’s commitment to international conventions, such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, accentuates the need for aligning national laws with global standards. Ensuring equal rights for foreign spouses, irrespective of gender, is in harmony with these commitments.
Moving Forward:
1. Legislative Reforms:
The recent judicial discourse calls for a critical review of existing citizenship laws. Legislative amendments that address gender-based disparities and ensure equal treatment for foreign spouses are essential to harmonize national statutes with constitutional principles and international commitments.
2. Inclusivity and Human Rights:
Recognizing the right of foreign spouses to choose their partners without facing discriminatory legal barriers is a vital step toward building an inclusive and rights-centric legal framework. Upholding human rights principles, including the right to family life, is imperative in shaping legal discourse around citizenship.
Conclusion:
The legal landscape concerning the citizenship of Pakistan for foreign spouses is evolving, guided by recent judicial pronouncements. The imperative of aligning national laws with constitutional guarantees and international commitments is evident. As Pakistan moves forward, fostering inclusivity, recognizing the equal rights of foreign spouses, and understanding the procedural aspects stand as essential pillars in shaping a legal framework that reflects contemporary principles of justice and human rights.
Pak-Lawyer Associates: Your Comprehensive Solution for Family Law and Spouse-Based Immigration Services in Lahore
Introduction:

In the intricate tapestry of legal services, Pak-Lawyer Associates emerges as a beacon of excellence, offering comprehensive solutions for both family law matters and spouse-based immigration services. Specializing in a range of cases including Court Marriage, Child Custody, Divorce, Khula cases, Child Maintenance, and spouse-based immigration, Pak-Lawyer Associates is your trusted partner for navigating the complexities of the legal landscape in Lahore.
Best Lawyer in Lahore for Family Cases:
Pak-Lawyer Associates has earned its reputation as the best in Lahore for family law cases. With a dedicated team of seasoned legal professionals, the firm is well-equipped to handle the intricacies of family matters, providing expert guidance and support to clients during challenging times.
Court Marriage:
For couples seeking legal validation for their union, Pak-Lawyer Associates ensures a seamless and efficient court marriage process. The firm’s expertise in navigating the legal requirements surrounding court marriages makes it the ideal choice for those embarking on this significant life journey.
Child Custody:
In emotionally charged Child Custody battles, Pak-Lawyer Associates stands out for its compassionate yet strategic approach. The legal team prioritizes the best interests of the child, working diligently to secure fair and just outcomes in custody disputes.
Divorce, Khula Cases, and Child Maintenance:
Recognizing the nuanced nature of divorce, Khula cases, and Child Maintenance proceedings, Pak-Lawyer Associates provides expert guidance rooted in a deep understanding of both Islamic and civil law. The firm’s commitment to transparency and efficiency ensures that clients can make informed decisions that shape their future.
Spouse-Based Immigration Services:
Beyond family law matters, Pak-Lawyer Associates extends its expertise to spouse-based immigration services. Navigating the intricacies of immigration law can be daunting, but with Pak-Lawyer Associates, clients benefit from a thorough understanding of immigration processes and a commitment to facilitating smooth transitions for families.
Why Choose Pak-Lawyer Associates?
1. Comprehensive Services: Pak-Lawyer Associates offers a one-stop solution for a wide range of legal services, including family law matters and spouse-based immigration services.
2. Expertise in Immigration: The firm’s proficiency in immigration law ensures that clients receive tailored guidance and support in matters related to spouse-based immigration.
3. Client-Centric Approach: With a focus on empathy and clear communication, Pak-Lawyer Associates places the client at the center of its practice, ensuring a supportive legal journey.
4. Proven Track Record: The firm’s track record of success and satisfied clients attests to its commitment to excellence and dedication to achieving positive outcomes.
Conclusion:
Pak-Lawyer Associates stands as a stalwart in the legal landscape of Lahore, offering unmatched expertise in family law matters and spouse-based immigration services. As the go-to solution for individuals navigating the complexities of the legal system, Pak-Lawyer Associates is committed to providing top-notch legal representation, ensuring that clients can confidently face the challenges ahead, whether they pertain to family matters or immigration issues.
How does the Family Court determine child maintenance?
How does the Family Court address the issue of child maintenance?
Are there specific guidelines and rules governing the determination of maintenance?
This blog aims to answer these questions and explore the parameters that the court considers when deciding on the financial support for minors or spouses.

How is child maintenance determined in family court?
Maintenance, as defined in Section 369 of Muhammadan Law by D.F. Mullah, encompasses the provision of food, clothing, and shelter for a child. However, this definition is not exhaustive and, in our perspective, should be interpreted more broadly to address the contemporary requirements of a minor’s social, physical, mental growth, upbringing, and overall well-being.
This extended interpretation should consider the family’s status, societal norms, and the educational needs of the child, which have gained paramount significance. It is crucial to assess the father’s capacity to pay while determining maintenance.
While maintenance goes beyond mere provisions of food, clothing, and shelter, it does not unconditionally encompass education at higher levels indefinitely. The key consideration is to determine the level of education necessary for the child, taking into account the family’s status and circumstances, enabling them to secure a livelihood through honest and decent means. It is insufficient to assume, for example, that a tradesman’s child can sustain themselves through casual work or dishonest activities. The child must be supported until they can independently earn a living in a manner consistent with their family’s standing.
According to Section 370 of the Muhammadan Law by D.F. Mullah:
1. A father is obligated to maintain his sons until they reach puberty and his daughters until they are married. However, he is not obliged to maintain adult sons unless they are incapacitated by infirmity or disease. The custody of the children by their mother during infancy does not exempt the father from the obligation to maintain them. The father is not obliged to maintain a child capable of self-maintenance through their own property.
2. If the father is indigent and unable to earn, the mother, if financially capable, is obliged to maintain the children as the father would be.
3. If both the father and mother are impoverished, the responsibility for maintaining the children falls on the grandfather if he is financially capable.
When determining the amount of maintenance, the court considers the educational needs, status, and general expenses of the minors, as outlined in PLD 2013 SC 557.
The court also assesses the likelihood of obtaining education and the ability to provide a stable, safe, and healthy environment for the minors. Without due consideration of these factors, the court cannot conclusively determine the amount of maintenance.
There is no rigid formula for determining maintenance, with the primary consideration being the father’s capacity to support the minors. The court takes into account various factors, including the actual needs of the minors, their living conditions, the manner in which the mother is providing for them, any special requirements, and the financial status of the father.
In determining the amount of maintenance, the court must take into consideration a range of factors, including:
1. The income and assets of the applicant.
2. The reasonable needs of the applicant, including those of the minor.
3. The income and assets of the respondent.
4. The standard of living maintained by both the respondent and the applicant.
5. The age of both the applicant and the respondent.
6. The physical and mental well-being of both the applicant and the respondent.
7. The necessary expenses for the education of the minor.
8. The financial obligations of the respondent, encompassing responsibilities towards other family members.
9. Any other pertinent factor deemed relevant to the case.
The court places particular emphasis on the father’s responsibility to meet the special needs of the minor, whether they be medical, physical, or related to specific educational requirements.
In sum, the court carefully considers all relevant circumstances and factors of the case to arrive at a fair determination of the amount of maintenance that the father is obligated to contribute towards the well-being of the minor.
GULL HASSAN KHAN ADVOCATE HIGH COURT
CEO, PAKLAWYER.COM PVT LTD
Legal Procedure for Khula in Pakistani Family Courts
Introduction:
The legal process for obtaining a Divorce or Khula Decree from the Family Court in Pakistan is designed to be accessible and straightforward, especially for wives seeking the dissolution of their marriages. The following delineates the Khula Procedure adopted by the Family Court in Pakistan.
Understanding Khula:
Traditionally, divorce is considered the prerogative of the husband in Islam. However, Islamic law recognizes situations in which a woman may exercise her right to free herself from the marital bond. The dissolution of marriage at the wife’s request in Islam can be pursued through two avenues:
1. Divorce Ordered by the Court: This option is available if the wife can demonstrate that she is facing harm within the marriage, empowering the court to grant a divorce under such circumstances.
2. Khula’: Unlike divorce ordered by the court, Khula’ does not necessitate the presentation of a specific reason. Islam acknowledges a wife’s inherent right to seek Khula’ without providing detailed justifications. Even a wife’s general dissatisfaction with her husband is considered a valid reason for seeking Khula’.
During the application for Khula’, the wife is not obligated to provide extensive reasoning for her decision, other than expressing her desire to end the marital relationship.
In essence, the Khula Procedure in the Family Court of Pakistan aims to facilitate the dissolution of marriages for women, providing a legal avenue for those seeking relief from an untenable marital situation.
Khula Procedure in the Family Court:
A wife can initiate the dissolution of her marriage through Khula by personally navigating the procedure or by enlisting the assistance of a lawyer. The process can be summarized as follows:
1. Preparation of Legal Case: A competent lawyer prepares a case brief according to the law, securing the legal interests of the wife and obtaining her signatures.
2. Filing the Case: The lawyer files the case before the court, prompting the court to summon the husband through notices (registered mail and TCS, etc.) and publication in a newspaper. The family court mandates the husband’s appearance within 10 to 15 days and provides an opportunity for him to file a written statement.
3. Court Appearance and Reconciliation: If the husband appears before the court, he can file a written statement. The court then sets a date for reconciliation (7 to 10 days).
4. Reconciliation Attempt: On the reconciliation date, the court endeavors to reconcile the parties. If reconciliation fails, the court issues the Khula decree.
Non-Appearance of Husband:
If the husband fails to appear before the court on the given date, the court issues an ex-parte decree in favor of the wife.
Divorce Effectiveness Certificate from Union Council:
Obtaining a Divorce Certificate is mandatory for updating marital status in NADRA and contracting another marriage. After receiving the Khula decree, the wife submits it to the relevant Union Council, along with a notice of intimation for the issuance of the divorce certificate. The Union Council, situated in the wife’s residential area at the time of filing the suit, then issues notices to the husband for reconciliation. If reconciliation fails or the husband remains absent from proceedings, the Union Council is obligated to issue the Talaq/Divorce Certificate after 90 days from the date of notice to the concerned Union Council. It’s important to submit the notice of intimation of Divorce/Khula promptly to initiate the 90-day period.